The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Branch of Government
Related Articles: The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Branch of Government
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Branch of Government. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Branch of Government

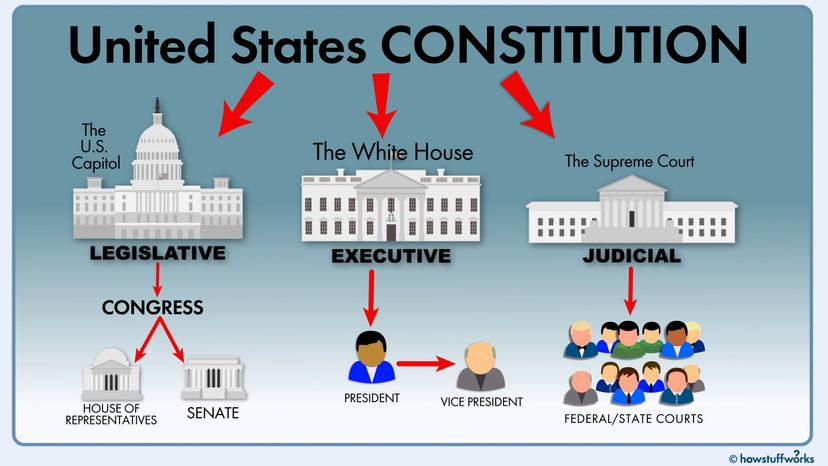
The United States Senate, one of the two legislative bodies of the federal government, plays a pivotal role in shaping American policy and law. Understanding its composition, the processes by which its members are selected, and the powers it wields is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of American politics.
The Structure of the Senate:
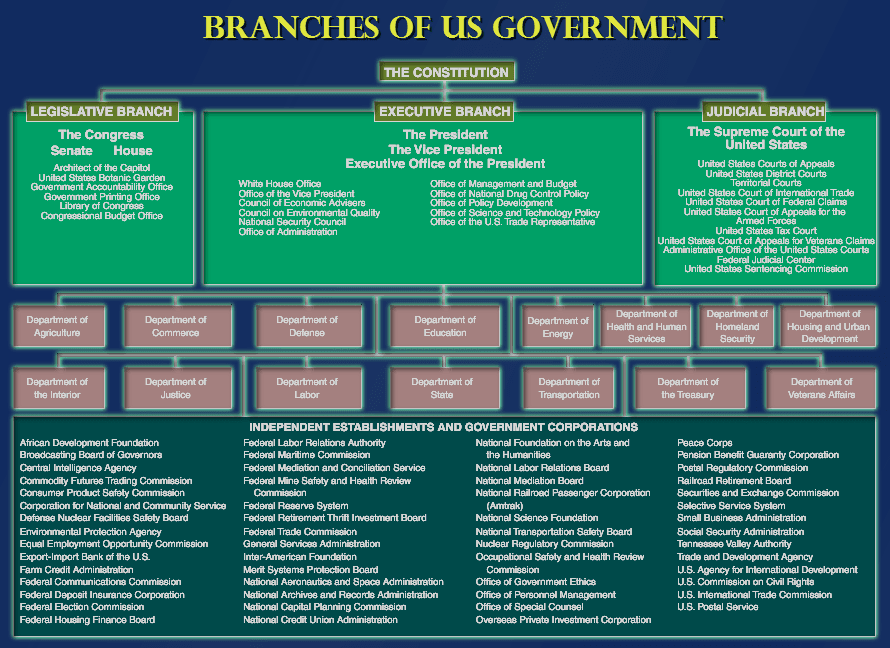
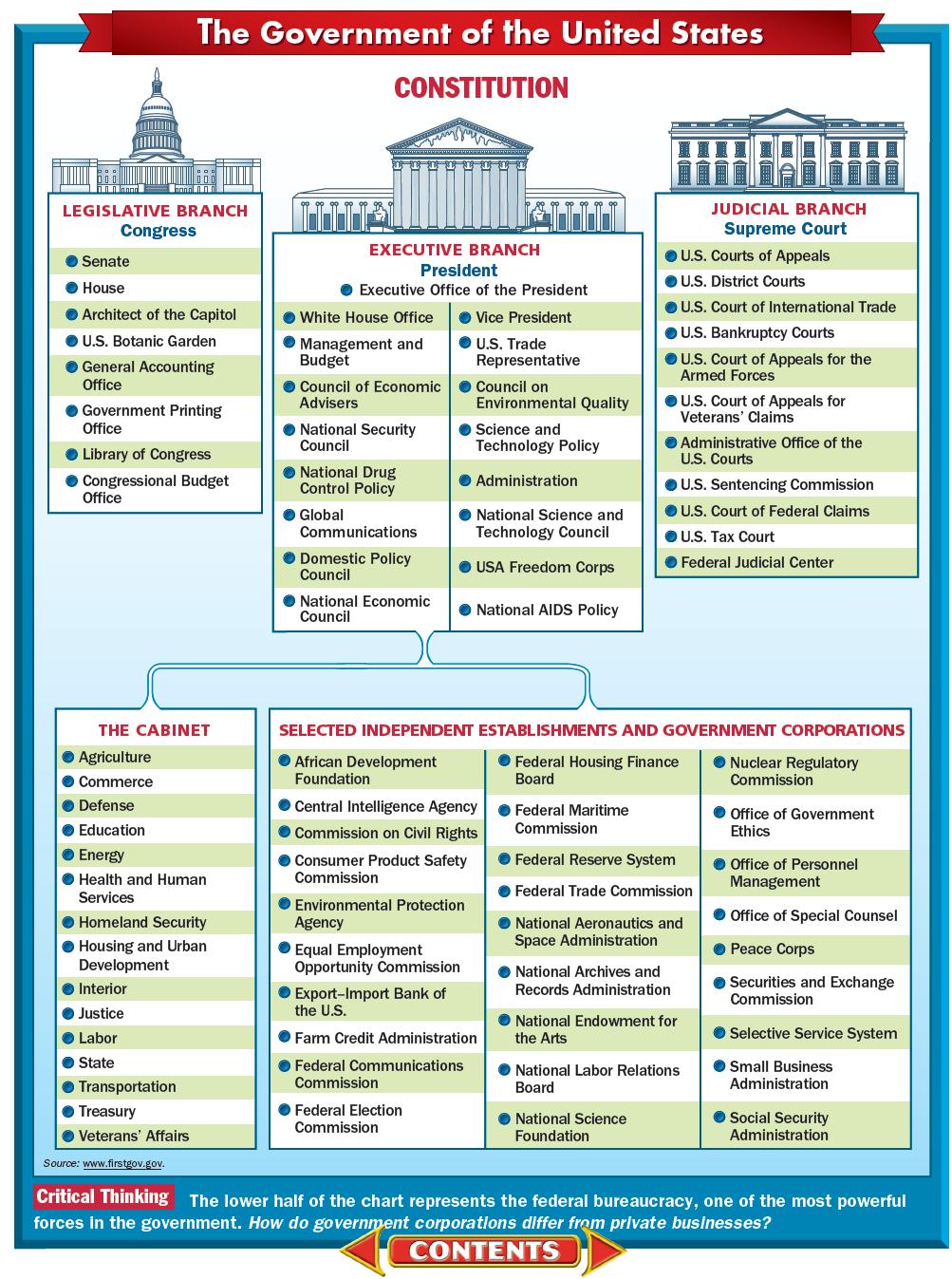
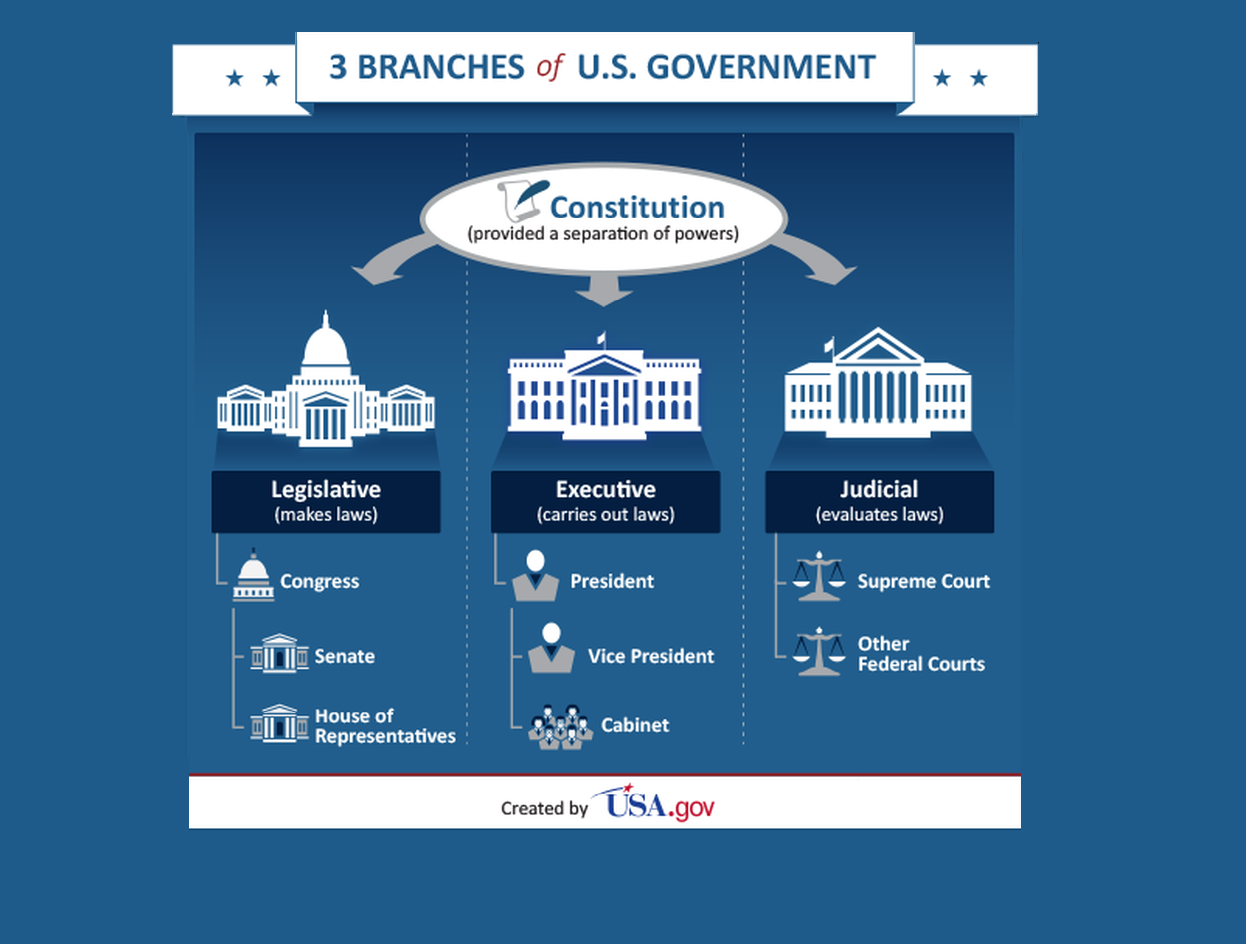
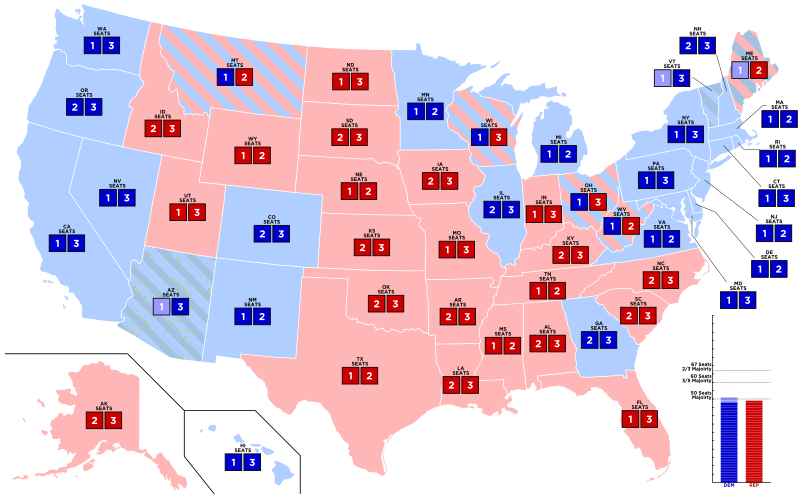
The Senate is composed of 100 members, two from each of the 50 states. This structure, enshrined in the Constitution, ensures equal representation for all states, regardless of their population size. This principle, known as the "equal suffrage" provision, stands in contrast to the House of Representatives, where representation is based on population.
Electoral Process:
Senators are elected by the citizens of their respective states. Unlike the House of Representatives, where members are elected every two years, Senators serve six-year terms. This longer tenure allows for greater stability and less susceptibility to short-term political pressures. The staggered terms, with one-third of the Senate up for election every two years, ensure that continuity and experience are maintained within the chamber.
Powers of the Senate:
The Senate possesses a wide range of powers, including:
- Legislative Power: The Senate, along with the House of Representatives, shares the responsibility of creating and enacting federal laws. Bills must be passed by both chambers before being sent to the President for signature.
- Confirmation Power: The Senate has the exclusive power to confirm presidential appointments, including cabinet members, federal judges, ambassadors, and other high-ranking officials. This power allows the Senate to scrutinize the qualifications and suitability of nominees.
- Treaty Ratification: The Senate holds the power to ratify treaties negotiated by the President with foreign governments. This power ensures that international agreements receive the consent of the legislative branch and reflect the interests of the nation.
- Impeachment Trials: The Senate has the sole power to try all impeachments. The House of Representatives has the power to impeach, but the Senate conducts the trial and determines whether to remove the accused from office.
The Importance of the Senate’s Composition:
The composition of the Senate, with its equal representation for all states and staggered terms, has a significant impact on the legislative process and the balance of power in the federal government.
- Regional Representation: The Senate’s structure ensures that the interests of smaller states are not overshadowed by those of larger states. This fosters a sense of balance and prevents a concentration of power in a few populous regions.
- Stability and Deliberation: The six-year terms and staggered elections contribute to a more stable and deliberative legislative body. Senators are less likely to be swayed by short-term political considerations, allowing for more thoughtful and long-term policy decisions.
- Checks and Balances: The Senate’s confirmation and treaty ratification powers serve as crucial checks on the executive branch, ensuring that the President’s power is not unchecked.
- Diversity of Perspectives: The Senate’s composition, with members representing a wide range of geographic, demographic, and ideological backgrounds, fosters a diversity of perspectives in the legislative process. This diversity can lead to more comprehensive and nuanced policy solutions.
Understanding the Senate’s Makeup: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How are Senators elected?
A: Senators are elected by the citizens of their respective states through popular vote.
Q: What is the length of a Senator’s term?
A: Senators serve six-year terms.
Q: How often are Senate elections held?
A: One-third of the Senate is up for election every two years.
Q: What are the primary powers of the Senate?
A: The Senate has the power to legislate, confirm presidential appointments, ratify treaties, and conduct impeachment trials.
Q: Why is the Senate’s composition considered important?
A: The Senate’s structure ensures equal representation for all states, promotes stability and deliberation, provides checks on the executive branch, and fosters a diversity of perspectives in the legislative process.
Tips for Understanding the Senate:
- Follow the news: Stay informed about current events and political developments, particularly those related to the Senate.
- Learn about your state’s Senators: Research the backgrounds, positions, and voting records of your state’s Senators.
- Engage with your Senators: Contact your Senators to express your views on important issues and participate in public hearings and town halls.
- Explore resources: Utilize online resources, such as the Senate website and nonpartisan organizations, to gain a deeper understanding of the Senate’s functions and the legislative process.
Conclusion:
The United States Senate, with its unique composition and powerful role in the federal government, stands as a vital pillar of American democracy. Its structure, powers, and the process of selecting its members all contribute to a system of checks and balances, ensuring that the interests of all citizens are represented and that the government operates with fairness and accountability. Understanding the makeup of the Senate is essential for comprehending the dynamics of American politics and the legislative process that shapes the nation’s laws and policies.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Composition of the United States Senate: A Vital Branch of Government. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
