Delving into the Building Blocks of Matter: A Comprehensive Look at the Atom
Related Articles: Delving into the Building Blocks of Matter: A Comprehensive Look at the Atom
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Building Blocks of Matter: A Comprehensive Look at the Atom. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Building Blocks of Matter: A Comprehensive Look at the Atom

The universe, in all its vastness and complexity, is built upon fundamental units known as atoms. These minuscule entities, invisible to the naked eye, are the foundation of every substance we encounter, from the air we breathe to the stars that illuminate the night sky. Understanding the composition of atoms is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of matter and the forces that govern its behavior.
The Atomic Structure: A Journey into the Heart of Matter
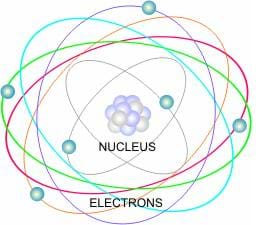
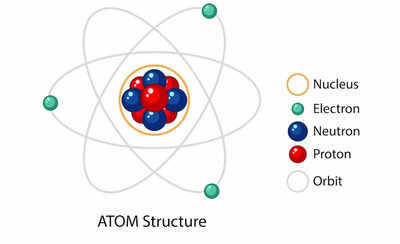
Atoms are not indivisible particles as once thought, but rather intricate systems composed of even smaller components. The fundamental constituents of an atom are:
-
Protons: These positively charged particles reside within the atom’s core, known as the nucleus. Protons are massive, contributing significantly to the atom’s overall mass. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus defines its atomic number, a key identifier that determines the element to which the atom belongs. For instance, all carbon atoms contain six protons, while all oxygen atoms contain eight.
-
Neutrons: Like protons, neutrons reside in the nucleus. They are neutral, carrying no charge. Neutrons contribute to the atom’s mass, but not its charge. The number of neutrons can vary within an element, giving rise to different isotopes. Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but differ in their neutron count. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, with six protons and six neutrons in carbon-12 and six protons with eight neutrons in carbon-14.
-
Electrons: These negatively charged particles orbit the nucleus in a cloud-like region known as the electron cloud. Electrons are significantly lighter than protons and neutrons, contributing minimally to the atom’s overall mass. The arrangement of electrons in the electron cloud determines an atom’s chemical properties and its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
The Quantum Realm: Unveiling the Electron Cloud
The electron cloud is not a chaotic swarm of particles but rather a structured region governed by quantum mechanics. Electrons occupy specific energy levels, and their movement is not described by classical physics but by probability distributions. These distributions, known as orbitals, represent the likelihood of finding an electron in a particular region of space around the nucleus.
The electron cloud is organized into shells, each corresponding to a specific energy level. Electrons in the outermost shell, known as valence electrons, are primarily responsible for an atom’s chemical behavior. These electrons are the ones involved in the formation of chemical bonds, leading to the creation of molecules and complex structures.
The Importance of Atomic Structure: Unlocking the Secrets of Matter
The arrangement and behavior of atoms are the foundation of chemistry, physics, and biology. Understanding the atomic structure allows us to:
-
Explain the properties of matter: The arrangement of electrons in the electron cloud determines an element’s chemical reactivity, melting point, boiling point, and other physical properties.
-
Predict chemical reactions: Knowledge of electron configuration helps predict how atoms will interact and form bonds, leading to the formation of new compounds and molecules.
-
Develop new materials: By manipulating the arrangement of atoms, scientists can create new materials with unique properties, leading to advancements in fields like medicine, electronics, and energy.
-
Understand the universe: The principles of atomic structure are fundamental to understanding the formation of stars, planets, and galaxies, providing insights into the origins and evolution of the cosmos.
FAQs about the Composition of Atoms
Q: What is the smallest particle of an element?
A: The smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element is an atom.
Q: How do atoms differ from each other?
A: Atoms of different elements differ in their number of protons, which determines their atomic number. This difference in proton count leads to variations in their chemical properties and behavior.
Q: Can atoms be broken down further?
A: While atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, they can be broken down into smaller particles known as subatomic particles. Protons and neutrons are themselves composed of quarks, while electrons are considered fundamental particles.
Q: How are atoms held together?
A: The nucleus of an atom is held together by the strong nuclear force, which is a powerful force that overcomes the electrostatic repulsion between protons. Electrons are attracted to the nucleus by the electrostatic force, creating a stable arrangement.
Q: How do atoms form molecules?
A: Atoms form molecules by sharing or transferring electrons between their valence shells. This sharing or transfer of electrons creates chemical bonds, holding the atoms together in a stable arrangement.
Tips for Understanding Atomic Structure
-
Visual aids: Utilize diagrams, models, and animations to visualize the structure of an atom and the arrangement of its components.
-
Analogies: Employ relatable analogies to simplify complex concepts. For instance, imagine the nucleus as the sun and the electrons as planets orbiting around it.
-
Focus on key concepts: Concentrate on understanding fundamental principles like atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical bonding.
-
Practice problem-solving: Engage in exercises and solve problems related to atomic structure to solidify your understanding.
Conclusion
The atom, with its intricate structure and fundamental role in shaping the universe, remains a fascinating subject of study. By delving into its components, we gain a deeper understanding of the world around us and unlock the potential for groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements. The journey into the realm of atoms is a journey into the very essence of matter itself.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-545863009-56a72c183df78cf77292fdbc.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Building Blocks of Matter: A Comprehensive Look at the Atom. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
